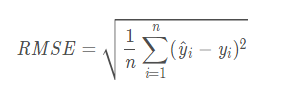1、MSE(均方误差)(Mean Square Error)
MSE是真实值与预测值的差值的平方然后求和平均。
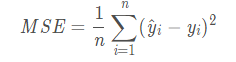
范围[0,+∞),当预测值与真实值完全相同时为0,误差越大,该值越大。
import numpy as np from sklearn import metrics y_true = np.array([1.0, 5.0, 4.0, 3.0, 2.0, 5.0, -3.0]) y_pred = np.array([1.0, 4.5, 3.5, 5.0, 8.0, 4.5, 1.0]) print(metrics.mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred)) # 8.107142857142858
2、
RMSE (均方根误差)(Root Mean Square Error)
import numpy as np from sklearn import metrics y_true = np.array([1.0, 5.0, 4.0, 3.0, 2.0, 5.0, -3.0]) y_pred = np.array([1.0, 4.5, 3.5, 5.0, 8.0, 4.5, 1.0]) print(np.sqrt(metrics.mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred)))
3、MAE (平均绝对误差)(Mean Absolute Error)

import numpy as np from sklearn import metrics y_true = np.array([1.0, 5.0, 4.0, 3.0, 2.0, 5.0, -3.0]) y_pred = np.array([1.0, 4.5, 3.5, 5.0, 8.0, 4.5, 1.0]) print(metrics.mean_absolute_error(y_true, y_pred))