作为一个开放源代码项目,Lucene从问世之后,引发了开放源代码社群的巨大反响,程序员们不仅使用它构建具体的全文检索应用,而且将之集成到各种系统软件中去,以及构建Web应用,甚至某些商业软件也采用了Lucene作为其内部全文检索子系统的核心。apache软件基金会的网站使用了Lucene作为全文检索的引擎,IBM的开源软件eclipse的2.1版本中也采用了Lucene作为帮助子系统的全文索引引擎,相应的IBM的商业软件Web Sphere中也采用了Lucene。Lucene以其开放源代码的特性、优异的索引结构、良好的系统架构获得了越来越多的应用。
Lucene作为一个全文检索引擎,其具有如下突出的优点:
(1)索引文件格式独立于应用平台。Lucene定义了一套以8位字节为基础的索引文件格式,使得兼容系统或者不同平台的应用能够共享建立的索引文件。
(2)在传统全文检索引擎的倒排索引的基础上,实现了分块索引,能够针对新的文件建立小文件索引,提升索引速度。然后通过与原有索引的合并,达到优化的目的。
(3)优秀的面向对象的系统架构,使得对于Lucene扩展的学习难度降低,方便扩充新功能。
(4)设计了独立于语言和文件格式的文本分析接口,索引器通过接受Token流完成索引文件的创立,用户扩展新的语言和文件格式,只需要实现文本分析的接口。
(5)已经默认实现了一套强大的查询引擎,用户无需自己编写代码即使系统可获得强大的查询能力,Lucene的查询实现中默认实现了布尔操作、模糊查询(Fuzzy Search)、分组查询等等。
lucene的索引结构

1. 准备工作
1.1 下载最新源码,https://github.com/apache/lucene-solr
1.2 编译,按照说明,使用ant进行编译(我使用了ant eclipse)
1.3.将编译后的文件导入到eclipse,sts或者idea中
2.新建测试类
public void test() throws IOException, ParseException {Analyzer analyzer = new NGramAnalyzer();// Store the index in memory:Directory directory = new RAMDirectory();// To store an index on disk, use this instead://Path path = FileSystems.getDefault().getPath("E:\\demo\\data", "access.data");//Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(path);IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);IndexWriter iwriter = new IndexWriter(directory, config);Document doc = new Document();String text = "我是中国人.";doc.add(new Field("fieldname", text, TextField.TYPE_STORED));iwriter.addDocument(doc);iwriter.close();// Now search the index:DirectoryReader ireader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);IndexSearcher isearcher = new IndexSearcher(ireader);isearcher.setSimilarity(new BM25Similarity());// Parse a simple query that searches for "text":QueryParser parser = new QueryParser("fieldname", analyzer);Query query = parser.parse("中国,人");ScoreDoc[] hits = isearcher.search(query, 1000).scoreDocs;// Iterate through the results:for (int i = 0; i < hits.length; i++) {Document hitDoc = isearcher.doc(hits[i].doc);System.out.println(hitDoc.getFields().toString());}ireader.close();directory.close();}private static class NGramAnalyzer extends Analyzer {@Overrideprotected TokenStreamComponents createComponents(String fieldName) {final Tokenizer tokenizer = new KeywordTokenizer();return new TokenStreamComponents(tokenizer, new NGramTokenFilter(tokenizer, 1, 4, true));}}
其中,分词使用自定义的NGramAnalyzer,它继承自Analyzer,Analyzer分析文本,并将文本转换为TokenStream。详细如下:
/*** An Analyzer builds TokenStreams, which analyze text. It thus represents a* policy for extracting index terms from text.* <p>* In order to define what analysis is done, subclasses must define their* {@link TokenStreamComponents TokenStreamComponents} in {@link #createComponents(String)}.* The components are then reused in each call to {@link #tokenStream(String, Reader)}.* <p>* Simple example:* <pre class="prettyprint">* Analyzer analyzer = new Analyzer() {* {@literal @Override}* protected TokenStreamComponents createComponents(String fieldName) {* Tokenizer source = new FooTokenizer(reader);* TokenStream filter = new FooFilter(source);* filter = new BarFilter(filter);* return new TokenStreamComponents(source, filter);* }* {@literal @Override}* protected TokenStream normalize(TokenStream in) {* // Assuming FooFilter is about normalization and BarFilter is about* // stemming, only FooFilter should be applied* return new FooFilter(in);* }* };* </pre>* For more examples, see the {@link org.apache.lucene.analysis Analysis package documentation}.* <p>* For some concrete implementations bundled with Lucene, look in the analysis modules:* <ul>* <li><a href="{@docRoot}/../analyzers-common/overview-summary.html">Common</a>:* Analyzers for indexing content in different languages and domains.* <li><a href="{@docRoot}/../analyzers-icu/overview-summary.html">ICU</a>:* Exposes functionality from ICU to Apache Lucene. * <li><a href="{@docRoot}/../analyzers-kuromoji/overview-summary.html">Kuromoji</a>:* Morphological analyzer for Japanese text.* <li><a href="{@docRoot}/../analyzers-morfologik/overview-summary.html">Morfologik</a>:* Dictionary-driven lemmatization for the Polish language.* <li><a href="{@docRoot}/../analyzers-phonetic/overview-summary.html">Phonetic</a>:* Analysis for indexing phonetic signatures (for sounds-alike search).* <li><a href="{@docRoot}/../analyzers-smartcn/overview-summary.html">Smart Chinese</a>:* Analyzer for Simplified Chinese, which indexes words.* <li><a href="{@docRoot}/../analyzers-stempel/overview-summary.html">Stempel</a>:* Algorithmic Stemmer for the Polish Language.* </ul>** @since 3.1*/
ClassicSimilarity是TFIDFSimilarity的封装,因TFIDFSimilarity是抽象方法,无法直接new出实例.这个算法是lucene早期的默认打分实现。
将测试类放入solr-lucene源码中,并进行debug,如果想要分析TFIDF算法,可以直接new ClassicSimilarity 然后放入IndexSearch,其它的类似。
3.算法介绍
新版的lucene使用了BM25Similarity作为默认打分实现。这里显式使用了BM25Similarity,算法详细。这里简要介绍一下:

其中:
D即文档(Document),Q即查询语句(Query),score(D,Q)指使用Q的查询语句在该文档下的打分函数。
IDF即倒排文件频次(Inverse Document Frequency)指在倒排文档中出现的次数,qi是Q分词后term
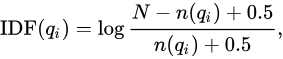 其中,N是总的文档数目,n(qi)是出现分词qi的文档数目。
其中,N是总的文档数目,n(qi)是出现分词qi的文档数目。
f(qi,D)是qi分词在文档Document出现的频次
k1和b是可调参数,默认值为1.2,0.75
|D|是文档的单词的个数,avgdl 指库里的平均文档长度。
4.算法实现
1.IDF实现
单个IDF实现
/** Implemented as <code>log(1 + (docCount - docFreq + 0.5)/(docFreq + 0.5))</code>. */protected float idf(long docFreq, long docCount) {return (float) Math.log(1 + (docCount - docFreq + 0.5D)/(docFreq + 0.5D));}
IDF的集合实现
@Overridepublic final SimWeight computeWeight(float boost, CollectionStatistics collectionStats, TermStatistics... termStats) {Explanation idf = termStats.length == 1 ? idfExplain(collectionStats, termStats[0]) : idfExplain(collectionStats, termStats);float avgdl = avgFieldLength(collectionStats);float[] oldCache = new float[256];float[] cache = new float[256];for (int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++) {oldCache[i] = k1 * ((1 - b) + b * OLD_LENGTH_TABLE[i] / avgdl);cache[i] = k1 * ((1 - b) + b * LENGTH_TABLE[i] / avgdl);}return new BM25Stats(collectionStats.field(), boost, idf, avgdl, oldCache, cache);}/*** Computes a score factor for a phrase.* * <p>* The default implementation sums the idf factor for* each term in the phrase.* * @param collectionStats collection-level statistics* @param termStats term-level statistics for the terms in the phrase* @return an Explain object that includes both an idf * score factor for the phrase and an explanation * for each term.*/public Explanation idfExplain(CollectionStatistics collectionStats, TermStatistics termStats[]) {double idf = 0d; // sum into a double before casting into a floatList<Explanation> details = new ArrayList<>();for (final TermStatistics stat : termStats ) {Explanation idfExplain = idfExplain(collectionStats, stat);details.add(idfExplain);idf += idfExplain.getValue();}return Explanation.match((float) idf, "idf(), sum of:", details);}
2.k1和b参数实现
public BM25Similarity(float k1, float b) {if (Float.isFinite(k1) == false || k1 < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("illegal k1 value: " + k1 + ", must be a non-negative finite value");}if (Float.isNaN(b) || b < 0 || b > 1) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("illegal b value: " + b + ", must be between 0 and 1");}this.k1 = k1;this.b = b;}/** BM25 with these default values:* <ul>* <li>{@code k1 = 1.2}</li>* <li>{@code b = 0.75}</li>* </ul>*/public BM25Similarity() {this(1.2f, 0.75f);}
3.平均文档长度avgdl 计算
/** The default implementation computes the average as <code>sumTotalTermFreq / docCount</code> */protected float avgFieldLength(CollectionStatistics collectionStats) {final long sumTotalTermFreq;if (collectionStats.sumTotalTermFreq() == -1) {// frequencies are omitted (tf=1), its # of postingsif (collectionStats.sumDocFreq() == -1) {// theoretical case only: remove!return 1f;}sumTotalTermFreq = collectionStats.sumDocFreq();} else {sumTotalTermFreq = collectionStats.sumTotalTermFreq();}final long docCount = collectionStats.docCount() == -1 ? collectionStats.maxDoc() : collectionStats.docCount();return (float) (sumTotalTermFreq / (double) docCount);}
4.参数Weigh的计算
/** Cache of decoded bytes. */private static final float[] OLD_LENGTH_TABLE = new float[256];private static final float[] LENGTH_TABLE = new float[256];static {for (int i = 1; i < 256; i++) {float f = SmallFloat.byte315ToFloat((byte)i);OLD_LENGTH_TABLE[i] = 1.0f / (f*f);}OLD_LENGTH_TABLE[0] = 1.0f / OLD_LENGTH_TABLE[255]; // otherwise inffor (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {LENGTH_TABLE[i] = SmallFloat.byte4ToInt((byte) i);}}@Overridepublic final SimWeight computeWeight(float boost, CollectionStatistics collectionStats, TermStatistics... termStats) {Explanation idf = termStats.length == 1 ? idfExplain(collectionStats, termStats[0]) : idfExplain(collectionStats, termStats);float avgdl = avgFieldLength(collectionStats);float[] oldCache = new float[256];float[] cache = new float[256];for (int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++) { oldCache[i] = k1 * ((1 - b) + b * OLD_LENGTH_TABLE[i] / avgdl);cache[i] = k1 * ((1 - b) + b * LENGTH_TABLE[i] / avgdl);}return new BM25Stats(collectionStats.field(), boost, idf, avgdl, oldCache, cache);}
相当于 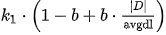
5.WeightValue计算
BM25Stats(String field, float boost, Explanation idf, float avgdl, float[] oldCache, float[] cache) {this.field = field;this.boost = boost;this.idf = idf;this.avgdl = avgdl;this.weight = idf.getValue() * boost;this.oldCache = oldCache;this.cache = cache;}BM25DocScorer(BM25Stats stats, int indexCreatedVersionMajor, NumericDocValues norms) throws IOException {this.stats = stats;this.weightValue = stats.weight * (k1 + 1);this.norms = norms;if (indexCreatedVersionMajor >= 7) {lengthCache = LENGTH_TABLE;cache = stats.cache;} else {lengthCache = OLD_LENGTH_TABLE;cache = stats.oldCache;}}
相当于
红色部分相乘
6.总的得分计算
@Overridepublic float score(int doc, float freq) throws IOException {// if there are no norms, we act as if b=0float norm;if (norms == null) {norm = k1;} else {if (norms.advanceExact(doc)) { norm = cache[((byte) norms.longValue()) & 0xFF];} else {norm = cache[0];}}return weightValue * freq / (freq + norm);}
其中norm是从cache里取的,cache是放入了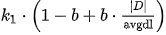
那么整个公式就完整的出来了
7.深入
打分的数据来源于CollectionStatistics,TermStatistics及freq,那么它们是哪里得到的?
SynonymWeight(Query query, IndexSearcher searcher, float boost) throws IOException {super(query);CollectionStatistics collectionStats = searcher.collectionStatistics(terms[0].field());//1long docFreq = 0;long totalTermFreq = 0;termContexts = new TermContext[terms.length];for (int i = 0; i < termContexts.length; i++) {termContexts[i] = TermContext.build(searcher.getTopReaderContext(), terms[i]);TermStatistics termStats = searcher.termStatistics(terms[i], termContexts[i]);//2docFreq = Math.max(termStats.docFreq(), docFreq);if (termStats.totalTermFreq() == -1) {totalTermFreq = -1;} else if (totalTermFreq != -1) {totalTermFreq += termStats.totalTermFreq();}}TermStatistics[] statics=new TermStatistics[terms.length];for(int i=0;i<terms.length;i++) {TermStatistics pseudoStats = new TermStatistics(terms[i].bytes(), docFreq, totalTermFreq,query.getKeyword());statics[i]=pseudoStats;}this.similarity = searcher.getSimilarity(true);this.simWeight = similarity.computeWeight(boost, collectionStats, statics);}
CollectionStatistics的来源
/*** Returns {@link CollectionStatistics} for a field.* * This can be overridden for example, to return a field's statistics* across a distributed collection.* @lucene.experimental*/public CollectionStatistics collectionStatistics(String field) throws IOException {final int docCount;final long sumTotalTermFreq;final long sumDocFreq;assert field != null;Terms terms = MultiFields.getTerms(reader, field);if (terms == null) {docCount = 0;sumTotalTermFreq = 0;sumDocFreq = 0;} else {docCount = terms.getDocCount();sumTotalTermFreq = terms.getSumTotalTermFreq();sumDocFreq = terms.getSumDocFreq();}return new CollectionStatistics(field, reader.maxDoc(), docCount, sumTotalTermFreq, sumDocFreq);}
TermStatistics的来源
/*** Returns {@link TermStatistics} for a term.* * This can be overridden for example, to return a term's statistics* across a distributed collection.* @lucene.experimental*/public TermStatistics termStatistics(Term term, TermContext context) throws IOException {return new TermStatistics(term.bytes(), context.docFreq(), context.totalTermFreq(),term.text());}
freq的来源(tf)
@Overrideprotected float score(DisiWrapper topList) throws IOException {return similarity.score(topList.doc, tf(topList));}/** combines TF of all subs. */final int tf(DisiWrapper topList) throws IOException {int tf = 0;for (DisiWrapper w = topList; w != null; w = w.next) {tf += ((TermScorer)w.scorer).freq();}return tf;}
底层实现
Lucene50PostingsReader.BlockPostingsEnum
@Overridepublic int nextDoc() throws IOException {if (docUpto == docFreq) {return doc = NO_MORE_DOCS;}if (docBufferUpto == BLOCK_SIZE) {refillDocs();}accum += docDeltaBuffer[docBufferUpto];freq = freqBuffer[docBufferUpto];posPendingCount += freq;docBufferUpto++;docUpto++;doc = accum;position = 0;return doc;}
8.总结
BM25算法的全称是 Okapi BM25,是一种二元独立模型的扩展,也可以用来做搜索的相关度排序。本文通过和lucene的BM25Similarity的实现来深入理解整个打分公式。
在此基础之上,又分析了CollectionStatistics,TermStatistics及freq这些参数是如何计算的。
通过整个分析过程,我们想要定制自己的打分公式,只需要实现Similarity或者SimilarityBase类,然后实现业务上的打分公式即可。
注意:实现了自己的Similarity类后solr不能直接使用,需要将其放到org.apache.solr.search.similarities,使用时
配置managed-schema如下:
<similarity class="solr.DavidSimilarityFactory"/> 注意,路径不是org.apache.solr.search.similarities.DavidSimilarityFactory,而是solr.DavidSimilarityFactory。若使用org.apache.solr.search.similarities.DavidSimilarityFactory则报错:
classnotfound
参考文献
【1】https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Okapi_BM25
【2】https://www.elastic.co/cn/blog/found-bm-vs-lucene-default-similarity
【3】http://www.blogjava.net/hoojo/archive/2012/09/06/387140.html
【4】https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/GEODE/Lucene+Internals
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/davidwang456/p/10439112.html
